Reverse Logistics
Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics refers to the process of managing and controlling the flow of goods, materials, and
products from their final destination back to their point of origin. It is a critical aspect of
supply chain management that focuses on the handling and disposition of goods that are returned or
not sold.
By recycling and repurposing materials, companies can reduce their environmental footprint and
conserve resources. Reverse logistics can also help companies save money by recovering value from
returned or defective products and minimizing the costs of waste disposal.

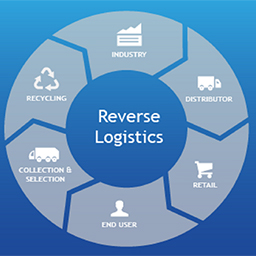

The Reverse logistics process typically involves several steps:
- Collection: This involves collecting the returned or unsold products from the customer or the point of sale. This may involve setting up a dedicated collection network, partnering with third-party logistics providers, or using postal or courier services.
- Sorting: Once the products are collected, they need to be sorted based on various criteria, such as their condition, value, and destination. This may involve inspecting and grading the products, separating them into different categories, and preparing them for further processing.
- Transportation: The sorted products need to be transported to their point of origin or to a facility for further processing. This may involve using various modes of transportation, such as trucks, trains, or ships, depending on the distance and volume of the products.
- Processing: The products need to be processed based on their condition and value. This may involve repairing, refurbishing, or repackaging the products to make them suitable for resale. Alternatively, the products may be disassembled and recycled or disposed of in an environmentally responsible manner.
- Redistribution: Once the products are processed, they can be redistributed to their point of sale or to a new destination. This may involve reselling the products through various channels, such as online marketplaces or discount stores, or donating them to charity.
- Reporting and Analysis: This may involve collecting data on key metrics such as product returns, processing times, and costs, and using this information to improve processes and reduce waste.

Our Other Services